中国科学院上海生命科学研究院生物化学与细胞生物学研究所胡红雨研究组解析了亨廷顿结合蛋白HYPB分子内部的WW结构域与多聚脯氨酸肽段所形成的自抑制结构,揭示了亨廷顿蛋白Huntingtin与HYPB相互作用的分子内调控机制。相关文章发表于2014年1月9日的《Structure》杂志上。 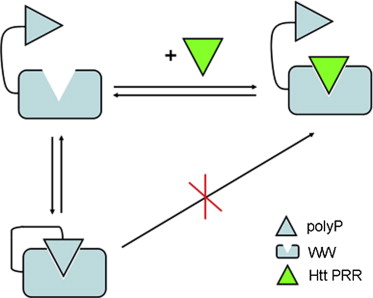 胡红雨研究组揭示亨廷顿结合蛋白HYPB/SET2自抑制分子机理 亨廷顿舞蹈症(Huntington’s disease)是一种典型的的神经退行性疾病,其主要病理特征是Huntingtin蛋白的多聚谷氨酰胺延伸突变引起神经细胞的退行性死亡,患者表现为运动、语言、智力方面的障碍。胡红雨课题组以前的工作解析了Huntingtin与亨廷顿结合蛋白HYPA/FBP11相互作用的结构基础(Y. G. Gao et al., Structure,2006,14, 1755),并阐明了异常谷氨酰胺延伸的Huntingtin蛋白积聚导致HYPA的细胞定位异常和剪接因子功能受损(Y. J. Jiang et al., J Biol Chem,2011,286, 25236)。 研究人员郜永光博士等首先发现了HYPB中的WW结构域被其附近的一段多聚脯氨酸肽段所抑制,然后用核磁共振方法解析了分别处于抑制和开放两种状态的WW结构域的溶液结构。三维结构分析表明该WW结构域与其它蛋白质的作用界面被其附近的多聚脯氨酸肽段覆盖,推测该肽段通过抑制WW结构域调节HYPB与Huntingtin蛋白的脯氨酸丰富区域之间的相互作用。该自抑制结构和分子内调控机制还得到核磁共振化学位移滴定以及细胞免疫荧光显微镜实验的证实。 该研究提出了Huntingtin与HYPB两蛋白质相互作用的一种新的调节模式,为将来进一步阐明亨廷顿舞蹈症的致病机理以及寻找药物靶点提供新的思路。 该项研究工作得到了国家科技部、基金委、中国科学院的经费支持。 原文摘要: Autoinhibitory Structure of the WW Domain of HYPB/SETD2 Regulates Its Interaction with the Proline-Rich Region of Huntingtin Yong-Guang Gao,Hui Yang,Jian Zhao,Ya-Jun Jiang,Hong-Yu Hu Huntington’s disease (HD) is an autosomally dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by expansion of polyglutamine (polyQ) in the huntingtin (Htt) protein. Htt yeast two-hybrid protein B (HYPB/SETD2), a histone methyltransferase, directly interacts with Htt and is involved in HD pathology. Using NMR techniques, we characterized a polyproline (polyP) stretch at the C terminus of HYPB, which directly interacts with the following WW domain and leads this domain predominantly to be in a closed conformational state. The solution structure shows that the polyP stretch extends from the back and binds to the WW core domain in a typical binding mode. This autoinhibitory structure regulates interaction between the WW domain of HYPB and the proline-rich region (PRR) of Htt, as evidenced by NMR and immunofluorescence techniques. This work provides structural and mechanistic insights into the intramolecular regulation of the WW domain in Htt-interacting partners and will be helpful for understanding the pathology of HD. |
胡红雨研究组揭示亨廷顿结合蛋白HYPB/SET2自抑制分子机理
时间:2014-01-16 15:47来源:生物帮 作者:未知 点击:
268次
顶一下
(0)
0%
踩一下
(0)
0%
------分隔线----------------------------
- 发表评论
-
- 最新评论 进入详细评论页>>
- 推荐内容
-
- 近五年毒理学研究机构的研究论文
5 印度的研究机构比较 在印度的研究机构(表 5 )中,印度科学...
- 美国出台BRAIN计划伦理问题报告
美国生物伦理问题研究总统委员会近日发布了首个报告 —— 将...
- 高胆固醇或致怀孕难
对某些怀孕困难的夫妇来说,问题也许与其胆固醇水平高有关。...
- 生命科学研究评价的新指标
文献计量学是以文献体系和文献计量特征为研究对象,采用数学...
- 脑科学计划何去何从?
题名: Whereto the mega brain projects? 作者: Mu-ming Poo 单位: Instit...
- 生物学标志记录岁月的痕迹
你知道自己衰老的速度如何么? 先别忙着去偷看网上“生物年龄...
- 近五年毒理学研究机构的研究论文
